Canada's expansive and complex geography poses significant challenges in delivering reliable electricity to remote and off-grid regions. The vast distances, coupled with the rugged terrain, complicate the extension of the electrical grid. As a result, many areas lack consistent access to power. This is particularly true in the northern territories and isolated communities where traditional energy solutions are costly and environmentally detrimental.
In areas well-served by the Eastern, Western, and Quebec grids, electricity is often generated through hydropower, which accounts for over 65% of Canada's electricity generation. However, this clean energy source is geographically limited, requiring proximity to water resources for the production of hydroelectricity.
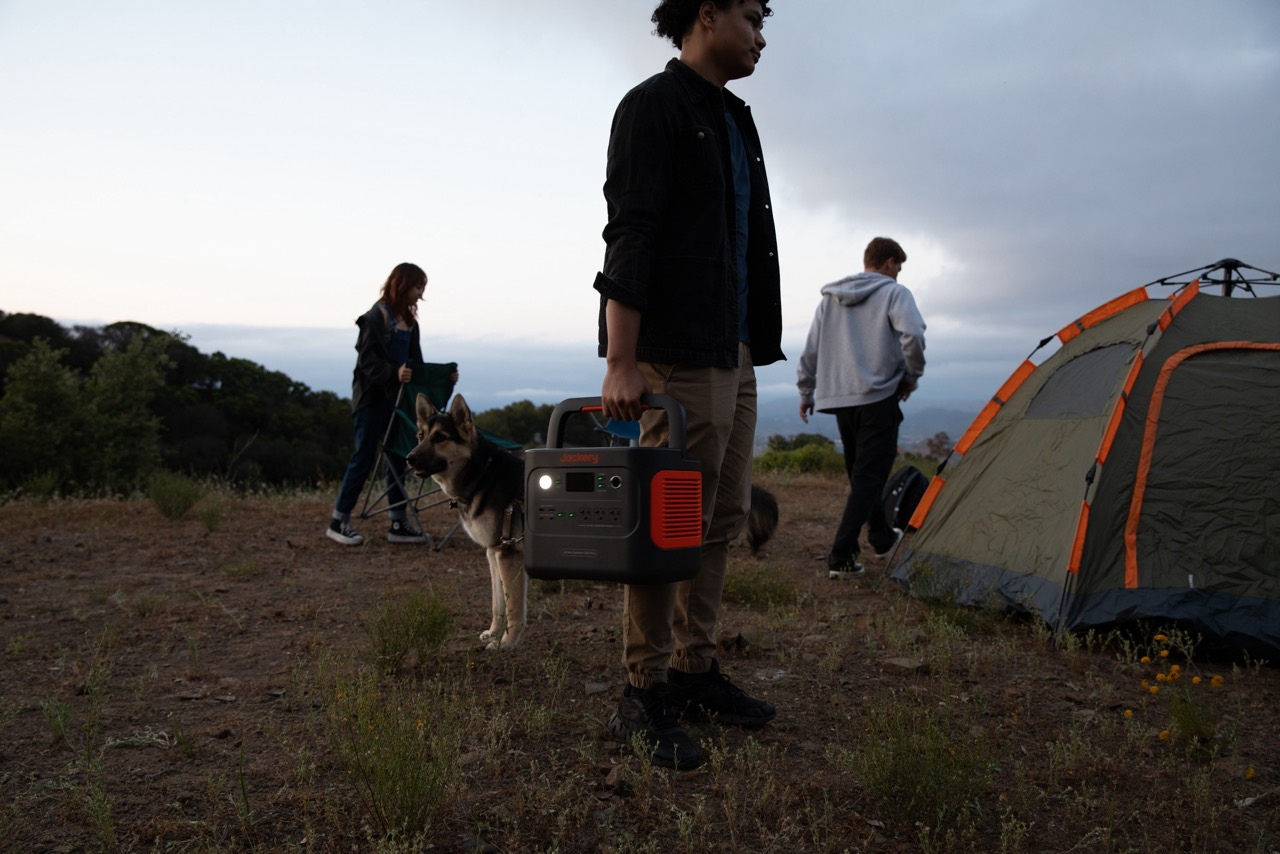
In response to these challenges, portable power stations, particularly those equipped with solar battery charger for backpacking, RV or balcony, have become an essential energy access solution for Canada. These systems provide renewable sources of energy, capable of meeting basic needs with electricity stored during the day.
This blog presents a comprehensive guide to knowing the reality of Canada's grid map in 2024 and the roles of solar generators in remote areas. As we delve into the details, we will discuss how these portable power stations are transforming the lives of those in Canada's most remote corners and shaping a more sustainable energy future for all.
Understanding Canada's Grid Map in 2024
Understanding the reality of Canada's grid map in 2024 is crucial for addressing the country's energy access disparities.
Canadian Power Grid Distribution
In 2024, Canada's grid map reflects a complex network of power distribution characterized by stark disparities in infrastructure development across different regions.
The Densely Well-equipped Grid Area
On one side, the densely well-equipped grid area is mostly in the south of Canada. Provinces like British Columbia, Ontario, and Quebec are most economic-prosperity and heavily-populated zones, which are characterized by extensive grid equipment. Equipped with a multitude of substations, transmission lines, and distribution networks, the grid net in these areas ensure a stable and reliable flow of electricity to the high-density residential and commercial sectors.
Besides, the infrastructure in these areas is typically more advanced, with innovative grid technologies that allow for better demand management, energy efficiency, and integration of distributed energy resources.
Area with Imperfect Power Grid Infrastructure
On the other hand, the less developed regions of the grid are primarily found in the remote and rural areas of Canada. Like the people in northern territories, especially in the Arctic Archipelago, the lack of adequate grid infrastructure makes them heavily rely on diesel generators and, where possible, small-scale hydroelectric or wind power facilities.
The transportation of fuel to these areas can be costly and challenging, particularly in harsh weather conditions, which can further exacerbate the issue of energy reliability. Besides, using fossil fuel would produce much waste and warm-house gas. It could deteriorate the fragile environment here and make the global warming worse.
Challenges of Electrifying Remote Canada
While urban centers and regions near hydroelectric dams enjoy robust grids, remote and off-grid communities grapple with the limitations of a patchy infrastructure. This disparity presents several key challenges:
High Costs and Fuel Dependence
Due to the dispersed population and harsh terrain, delivering traditional grid infrastructure to remote areas is expensive. Many communities depend on costly and polluting diesel for their electricity.
Limited Economic Opportunities
Electricity is a cornerstone of economic development. Without a stable supply of power, businesses can’t operate efficiently, and attracting new investment is difficult. This lack of economic opportunity can lead to a cycle of poverty and hinder the overall development of remote regions.
Impact on Basic Needs and Quality of Life
The most fundamental aspects of daily life are affected. For example, it influences people’s communication. Limited bandwidth and intermittent connectivity impede seamless communication, affecting productivity and social cohesion. Vulnerable communities bear the brunt, facing inequalities in accessing vital services and information. Bedies, it also downgrade the life’s quality. One of the obvious flaws is that heating during harsh winters can be challenging.
Environmental Concerns
Diesel reliance contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and local air pollution. Fossil fuels and other unclear resources not only impact the health of residents but also run against Canada's goals for environmental sustainability.
The Energy Situation of Nunavut
Nunavut, Canada's northernmost territory, encompasses vast, remote landscapes and is home to predominantly Inuit communities. Despite its natural beauty, Nunavut faces significant challenges in infrastructure, particularly its power grid. The region's harsh Arctic climate, with long, dark winters and permafrost terrain, complicates traditional grid development.
According to a report by the Canadian Energy Regulator (CER), over 280 communities in Canada (around 200,000 people) need to be hooked up to the North American power grid or natural gas distribution systems. These remote, off-grid communities mainly rely on pricey diesel power, which poses a tough challenge for their daily lives.
Take Nunavut, for instance, where nearly all the electricity is generated from diesel imported during the summer and then stored for use throughout the year. This dependence on one fuel makes the region vulnerable to fluctuations in diesel prices and supply disruptions.
On top of that, running on diesel comes with high operating costs, not just for the fuel itself but also for transportation and storage costs. These steep costs eventually get passed down to the locals, leading to residents dealing with sky-high electricity bills.
Diesel power generation also harms the environment. Its greenhouse gas emissions worsen climate change and can harm local ecosystems and wildlife habitats.
Introducing Solar Generator: Powering the Remote Aera
With advancements in solar panels & battery storage, or called it solar generator, the residence in remote communities can gain an economical, powerful but still sustainable solution to compared with the conventional approaches of power generation. With its portable solar panels, it is an economical way to generate electricity using endless sun power. Follow the information below to find out more about these portable power stations:
Functions
- Solar panels convert sunlight into renewable and clean energy, reducing reliance on polluting diesel generators and fostering environmental sustainability.
- These compact units are designed for easy transportation and deployment.
- Portable power stations cater to individual needs in various capacities. Some can power essential appliances, while larger units can handle more demanding applications.
An Alternative of On-Grid Power Supply
Portable power stations with foldable solar panels offer a resilient alternative to traditional grid connections in remote Canadian communities like Nunavut. Unlike unreliable grids reliant on diesel generators, these systems harness solar energy for sustainable electricity generation. Their portability and independence empower communities, reducing environmental impact and mitigating disruptions.
By integrating renewable energy, solar system battery bank with panels enhance sustainability and resilience on power supply, crucial in harsh climates. Additionally, they support emergency response efforts, ensuring essential services during disasters.
Overall, portable power stations address flaws of traditional grids, fostering sustainability, resilience, and empowerment in remote Canadian communities.

How to Choose Your Solar-Powered Portable Station
Solar-powered portable power stations offer a convenient solution for off-grid living in remote communities. Here's a guide to assessing your energy needs, evaluating site suitability for solar panels, and ensuring a smooth installation:
Assessing Your Energy Needs
- Power Consumption:List the appliances and devices you plan to power with your station. Research their wattage and usage time to estimate your daily power consumption in watt-hours (Wh).
- Buffer and Headroom: Factor in a 20-30% buffer to account for unforeseen needs and inefficiencies. Consider future upgrades when selecting a station with a higher capacity than your current needs.
Site Suitability for Solar Panels
- Sunlight Exposure:Choose a location with as long direct sunlight per day as possible for optimal solar panel performance. South-facing areas are ideal in the Northern Hemisphere. Avoid areas with significant shade from trees, buildings, or other obstacles throughout the day.
- Space Availability:Measure where you plan to deploy the solar panels. Consider the unfolded size of the panels and ensure they have sufficient space for optimal positioning.
Installation Considerations
- Read the Manual: Each portable power station has its own set of instructions. Carefully review the manual before starting the installation process.
- Safety First:Ensure proper polarity to avoid damage when connecting the solar panels to the station.
- Angling the Panels: To maximize sun exposure, adjust the solar panel tilt angle seasonally.Consult the manufacturer's recommendations or online resources for optimal panel positioning based on location.
Additional Tips
- Research and Compare: Before purchasing, look for reliable brands and compare features like battery capacity, wattage output, solar panel efficiency, and warranty terms.
- Scalability:Consider future needs. Some systems allow additional solar panels to increase your power generation capacity.
- Professional Help:It is always recommended that you consult a qualified electrician for complex installations or if you need clarification on any aspect of the process.
Recommending Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus
While various portable power stations with solar panels exist, our Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus is a compelling option for remote communities seeking reliable and sustainable energy solutions. Let's explore why this particular model might be an excellent fit for your off-grid needs:
- High Capacity
Its battery module, the Jackery Explorer 1000 Plus Portable Power Station has a 1260Wh capacity, which could satisfy the energy needs of off-grid living, offering sufficient power to run essential appliances and electronics in remote locations without .
- Robust Output Capabilities
With a peak output of 2000W, our unit can handle even moderately demanding appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and power tools. This versatility makes it suitable for various applications in remote settings.
- Expandable Power
A unique feature is its expandability. Up to three additional battery packs (sold separately) can be connected to create a whopping 5kWh system. This expandability is particularly beneficial for extended periods, like winter, when the demand for electricity is higher.
- Sustainable Solar Power
By pairing this portable power station with these high-efficiency panels, communities can harness clean and renewable solar energy to recharge the unit, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing impact on this fragile land.
- Mobility
Our Jackery Solar Generator 1000 Plus can be regarded as a mobile socket. With its compact, portable and embedded hurdle design, it is easy to transport and deploy wherever needed within the community, providing outstanding portability wherever you need the power.

Conclusion
As a leader in portable power solutions, Jackery offers a range of portable power stations equipped with foldable solar panels to meet the diverse energy needs of individuals and communities in remote and off-grid areas of Canada.
Recognizing the country's vast geography and the challenges it presents in terms of electricity access, our products are engineered to provide reliable and sustainable energy solutions in areas not covered by the primary electrical grid. In 2024, you can create your electricity from solar power stations whether you are out of the grid map in Canada with our portable power stations.












































![[Add-on] Jackery Manual Transfer Switch for Explorer 5000 Plus](http://ca.jackery.com/cdn/shop/files/add-on-jackery-manual-transfer-switch-for-5000-plus-240V.webp?v=1757043692&width=170)